Note: This post originates from collaboration and discussions between Melissa, Punya, and Nicole. However, it is written from Nicole’s point of view as a current student, reflecting our efforts to explore student perspectives when considering the integration of AI in education.
Newsweek recently reported how a former educator and curriculum designer devised a strategy for “catching” students using ChatGPT for essays by embedding a hidden sentence in the essay prompt. Some would argue that this tactic will help hold students accountable for academic integrity or support student conversations about these matters.
On the other hand, this can be seen as an ongoing cat-and-mouse game that at heart reflects sense of distrust that educators have in their students. In this way, this story exemplifies the punitive nature of an educational culture marked by student surveillance.
For the past two years, educators and institutions have discussed, ad nauseam, the ethical use of genAI and debated whether it undermines academic integrity. However, I am sometimes frustrated by the often one-sided, maybe even hypocritical, nature of this discussion. At one level, we have workshops and seminars, futurists and early adopters arguing for the efficiency benefits that teachers will receive from using these tools for lesson planning, grading, sending emails and more. At the same time, we have a counter-push that condemns student use of genAI to complete classwork more efficiently. This attitude is even embedded into some tools, such as the Harmonize discussion software that offers “AI prompt and rubric generation” for the instructor and “AI Detection” for the student.
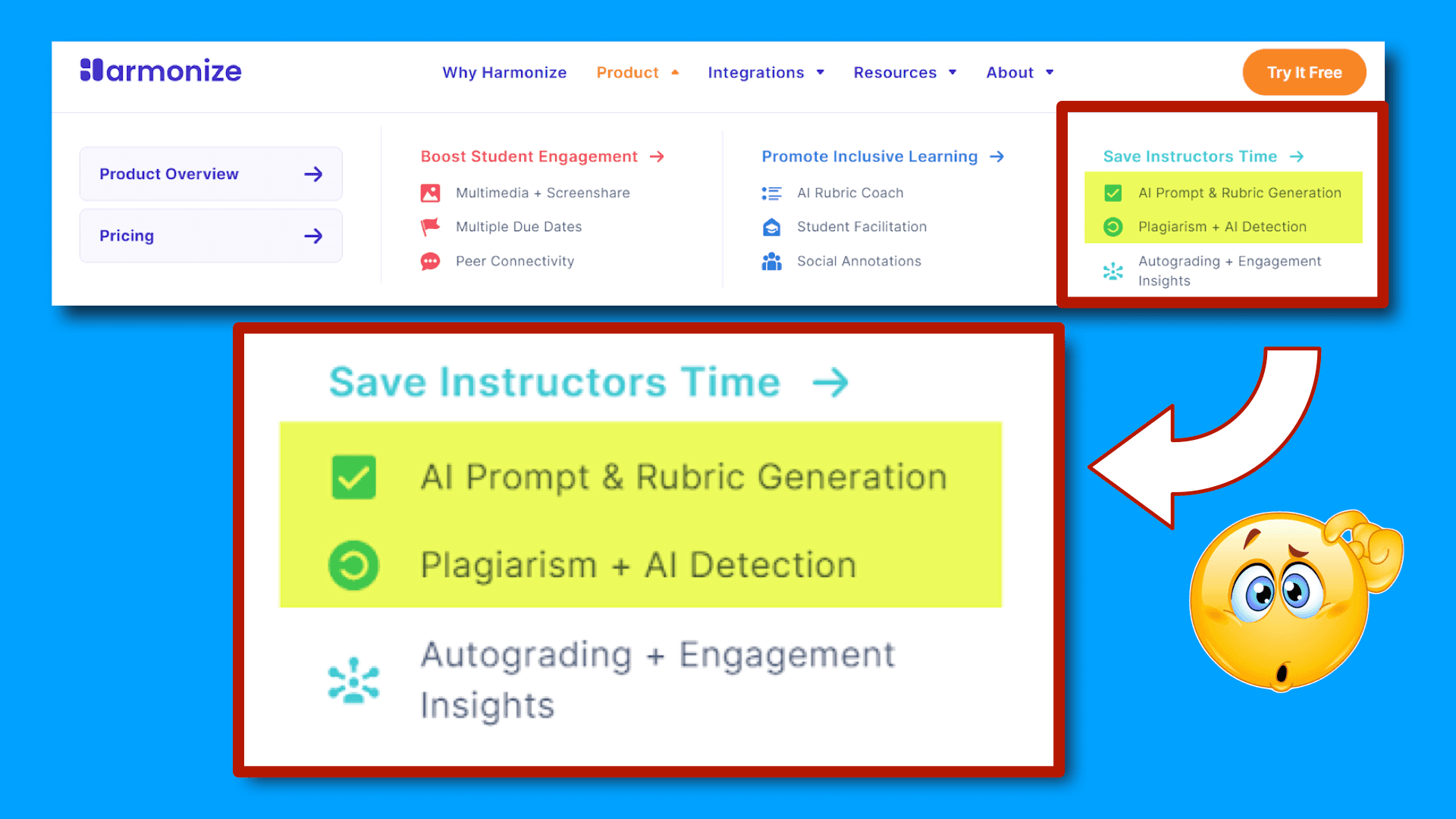
I have begun to wonder why students’ ethical use of genAI dominates these conversations. As a student, I can attest that assuming that students are just out to cheat can feel demeaning and hurtful.
Instead of wallowing in this debate, it made more sense for me to reflect on my own ethical compass and decision-making process about using generative AI. I am sensitive to the fact that my choices may not be yours, but I do think that this form of critical AI reflection (as mentioned in this post by Melissa) is the way forward.
What uses of genAI feel ethically good?
- Refining an idea: eg. engaging in a back-and-forth dialogue with GenAI to improve, build on, or challenge an idea, attaching relevant resources when appropriate
- Trying to write something standardized … trying to do “what works” … to build on what has been done before: eg. revising a draft to sound more academic or more tailored to a specific domain or framework
- Brainstorming with genAI as a partner: eg. exploring and generating new possibilities through carefully designed prompts with parameters specific to my goals
- Reclaiming my time when under a lot of pressure to protect my mental health and wellbeing: eg. using genAI to help me summarize articles (before fact checking these summaries) for my own learning
- Easing my anxiety around sending emails that need to just get sent: eg. typing out the key ideas of an email then using genAI to polish it and improve its etiquette, or simply asking geAI if it looks good before sending
What doesn’t feel ethically good?
- Using it for analysis before I have done my own analysis (in my view, this steals the opportunity to struggle and learn for myself)
- Using it on a task that would be better if it were in my unique, context-specific, humanly flawed voice (I see this as robbing others of my authentic contributions)
- Endeavors that are meant to be forms of self-expression (I view this as stealing the joy of creativity from myself)
What does this mean for my writing?
- Refocus human-generated writing on writing that is analytical, carries a unique voice, and is a form of self-expression.
Obviously, this one reflection should not be used to create broad institutional policies. Rather, I share it as an example of a formative individual reflective process.
What if…
…we encourage students to likewise engage in developing their own codes and implications for ethical AI use?
…we discussed these personal codes and their societal implications in community with one another?
…we took the necessary steps to promote transparency and disclosure of genAI use among our student body by setting aside judgment and distrust?
…we took long-awaited steps to dismantle educational hierarchies of power?
This suggestion doesn’t mean a genAI free-for-all. Rather, I offer this idea as one possible path for holding space for students to explore these ideas for ourselves. Of course, educators and institutions will still need to hold students accountable, but we must also cultivate relationships of trust. We must hold ourselves as educators and institutions accountable for truly, deeply, and critically supporting the learning of the remarkable humans we call our students.
By reflecting together, we can explore what we value in education, how we want to learn, and why we use AI as educators and learners.


0 Comments